Cloud cost optimization is often misunderstood, with many companies mistaking it for a purely financial pursuit. While cloud cost optimization (CCO) does seek to eliminate waste from cloud expenditures, it also helps to identify inefficient cloud computing processes and reduce shadow IT. A well-managed CCO strategy can also improve data handling processes, leading to higher data quality and greater efficiency for ML and generative AI models, which ultimately helps companies achieve better AI outcomes.
For quick reference, we offer a concise working definition.
Cloud Cost Optimization:
The process of ensuring that a company is only utilizing the cloud resources they actually need while optimizing those resources to reduce overall spending, improve cloud-based operational efficiency, and better support the business’s needs.
This article serves as the ultimate guide to cloud cost optimization, in which we’ll answer fundamental questions about cloud cost management challenges, strategies, tools, and platforms. In addition, we offer some actionable next steps for those looking to get started. Use the links below to jump ahead to specific topics.
| Table of Contents |
|---|
What challenges are solved by cloud cost optimization?
While cloud computing typically helps to reduce IT spending, the on-demand scalability and rich cloud product ecosystem make it easy for costs to spiral out of control.
Cloud cost management challenges solved by cco
| Challenge | Description |
|---|---|
| Fluctuating monthly bills | The ability to add or remove resources – either on-demand or automatically – makes it difficult to predict cloud costs. A bill that fluctuates every month can make setting accurate annual cloud expenditure budgets extremely difficult. |
| Underutilization of cloud resources | Companies often deploy cloud virtual machines (VMs) with more CPU power than required for the task at hand rather than reallocating resources where they’re needed or shutting them down to reduce monthly costs. |
| Shadow IT | Many departments purchase their own cloud services to address individual use cases without involving or notifying IT. This creates “shadow IT,” a scenario in which IT can’t track the costs (or security risks) of all the software and infrastructure the business uses. |
| Complex billing | The total cost of cloud services isn’t always obvious, as individual features add hidden fees, and resource prices fluctuate as you reach different scaling benchmarks. This complexity can exacerbate cloud budget inaccuracies. |
| Disappointing performance | Companies often find their operational performance in the cloud doesn’t meet the expectations set during the sales process due to inefficient data handling or how they’ve configured their deployment, so they don’t get the results they paid for. |
| Orphaned resources | Sometimes, IT teams don’t decommission containers and VMs correctly, leaving orphaned resources like compute instances and unmounted storage disks that companies pay for even when they aren’t actively used. |
| Rising data storage costs | Cloud data storage prices keep rising while businesses are generating more data each year. As a result, data storage costs begin to rival compute in terms of the biggest cloud expenses. |
Cloud cost optimization allows companies to “trim the fat” on their cloud spend by identifying mismanaged resources and right-sizing their services. CCO discovers all the cloud services in use across an organization to reduce security risks and uncovers all the surprise charges and hidden fees for greater billing visibility. A well-managed cloud cost optimization strategy also finds data management inefficiencies and identifies lower-cost resource options to help companies get the most out of their cloud investment.
Despite the effectiveness of CCO practices, many companies are hesitant to adopt them – primarily out of fear they will disrupt existing processes the company sees as valuable. However, cloud cost optimization can help:
- Manage cloud spending. Cloud cost optimization practices identify resource inefficiencies and redundancies in your cloud spending to eliminate waste. For example, CCO looks for ways to reduce unnecessary compute and data storage utilization to optimize infrastructure costs, like shutting down orphaned instances and compressing data. CCO can also identify expensive services and resources that could be replaced by lower-cost options that still support the business’s requirements.
- Increase operational efficiency. The goal of cloud cost optimization is to make operations more efficient, which means identifying and preserving processes that are working while refining, replacing, or eliminating those that aren’t. For example, CCO may uncover inefficiencies in VM provisioning and decommissioning workflows that could benefit from automation while simultaneously identifying that an existing manual (human) checkpoint is necessary to ensure resource costs don’t spiral out of control.
- Improve visibility & accountability. Cloud cost optimization makes it easier to track all the cloud services an organization uses to reduce shadow IT and improve overall accountability for cloud spending. This allows IT to create more realistic cloud budgets and gives finance teams greater visibility into technology costs across the company.
- Maximize cloud performance. Cloud cost optimization helps companies identify inefficiencies in resource configurations and data handling processes. For example, CCO data compression techniques reduce the amount of redundant or unnecessary data flowing between instances, freeing up additional bandwidth for more critical workloads. Cloud cost optimization ensures businesses get the speed, performance, and reliability they pay for.
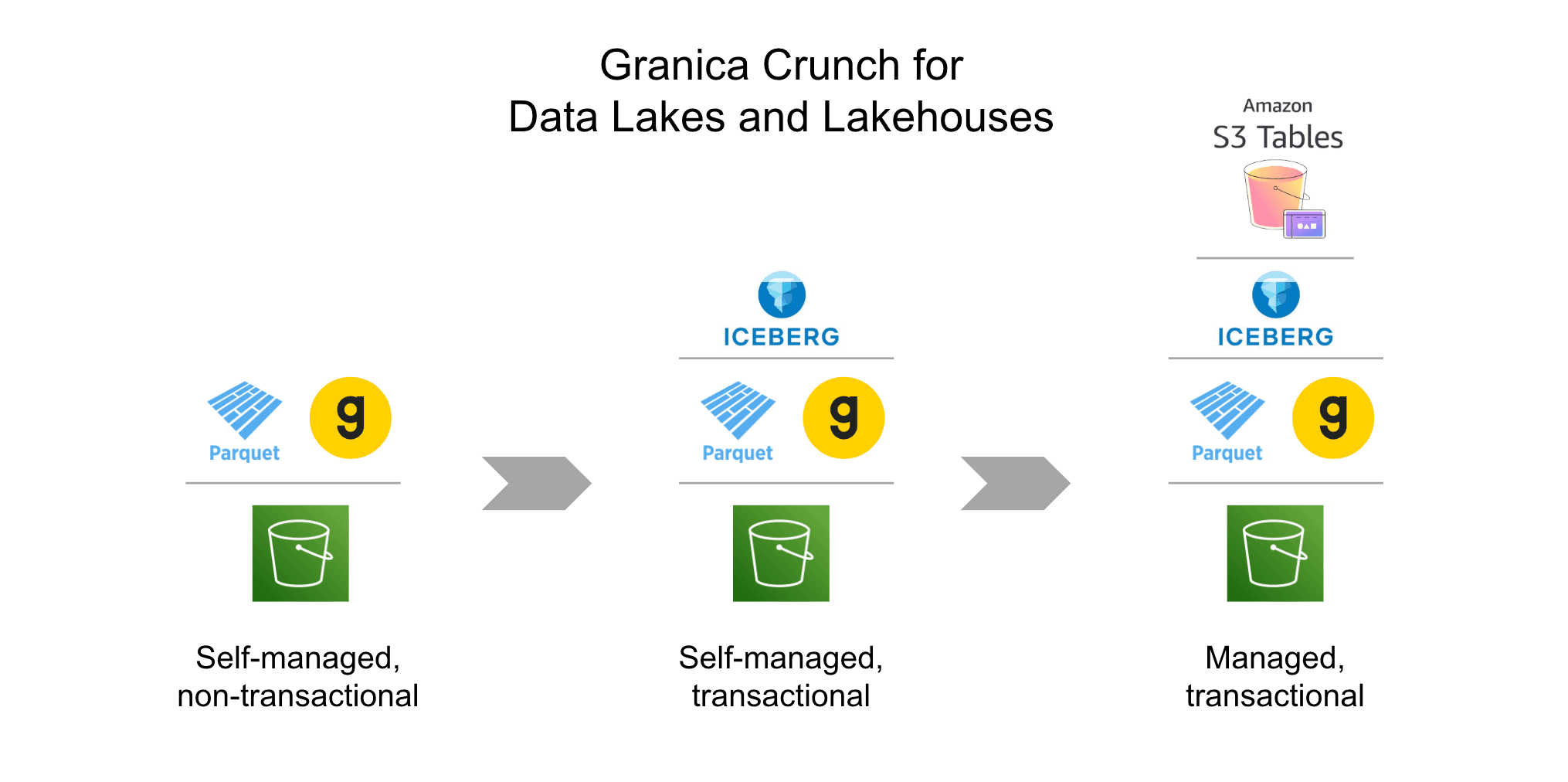
Granica Crunch is a cloud cost optimization service for cloud data lakes and data lakehouses, focused on the cost to store data. Use our cloud cost savings calculator to see how Crunch can shrink your data expenses and improve the value of your cloud investment.
Cloud cost optimization strategies
Cloud cost optimization can be purchased as a service, but hiring a team of CCO specialists is often a decision that management hesitates to execute; after all, the point is to save money rather than spend it. There are a number of cloud cost optimization strategies that in-house teams can implement to optimize cloud costs before taking further steps.
Cloud cost optimization strategies: A brief breakdown
| Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Utilize reserved instances / Savings plans | Taking on a longer reservation with a cloud service provider results in a lower price. These pricing models usually take the form of a 1- to 3-year contract in which the company agrees to pay a certain dollar amount for a specific amount of data. As such, they are ideal for more predictable workloads but don’t provide much flexibility. |
| Identify underutilized / idle resources | The greatest drain on your cloud spending is the funds wasted on cloud resources that teams are either a.) not using fully, or b.) not using at all. Right-sizing resources allows companies to reallocate processing power, storage, and bandwidth where they’re needed most for optimal performance and to fully realize the potential cost savings promised by the cloud. |
| Data compression | Data storage is a significant cloud expense, so optimally compressing columnar data sets in formats such as Apache Parquet and ORC stored in cloud data lakehouses, is one of the easiest top-line ways to cut cloud costs. Compression reduces the physical size of lakehouse files, allowing companies to reduce both at-rest storage and data transfer costs without having to sort through their data to determine what’s valuable and what isn’t. Beyond reducing costs, efficiently compressed files can also speed queries and data loading times, a significant benefit for analytics, AI and ML teams. |
| Data tiering / deletion | Identifying your most valuable data to keep in fast, easily accessible storage tiers allows you to place lower-priority data in less expensive (but also less accessible) long-term archival tiers. For truly unnecessary and no longer valuable data, the best strategy is simple deletion. Knowing when data is safe to delete typically requires specialized data governance processes and tools. Actively used data, such as for analytics, AI, and ML, typically is not a good candidate for tiering so look to use OSS compression instead. |
| Track resource spending and implement chargeback | Cloud cost optimization teams often implement “cost allocation tags” to track cloud spending on specific resources. This allows companies not only to track their overall cloud spending, but also to identify which departments utilize the lion's share of cloud resources through visibility models that increase transparency and efficient accounting practices. |
In addition, it’s important to ensure that teams are reviewing these implementations on a regular basis and adjusting their strategy accordingly. This is especially true for industries in which policy and regulation are constantly changing (e.g., technology, healthcare, finance), where your current cloud cost optimization strategy may run counter to new industry standards.
Frequent cloud implementation audits are also crucial whenever you see big shifts in cloud usage, for example, when multiple on-premises workloads migrate to the cloud. New product releases or technology initiatives, like AI and machine learning, also present ideal opportunities for review as they typically generate a number of new cloud workloads.
What metrics should i track for best cloud cost optimization practices?
There are numerous key performance indicators (KPIs) used to measure the success of cloud cost reduction and optimization strategies, including:
Cloud cost optimization kpis
| Category | KPI | Formula |
|---|---|---|
| Cost efficiency | Total cloud spend: Total sum of all cloud-related expenses over a specific period (typically calculated quarterly/annually). | Total = (Cost of services + cost of data transfer + additional fees) |
| Cost per workload: Total cost associated with a specific application or microservice. | Total cost of applications / # of applications. | |
| Utilization rates | Resource utilization: % of total resource capacity being used within a company’s tech architecture. | (Used resource capacity/total resource capacity) x 100 |
| Cost allocation/ distribution | Cost by service or resource: How much of the total budget a specific resource costs the company. | Cost of specified resource / total cloud spend |
| Cost savings post optimization: Total spend reduction achieved through current optimizations. | Spend prior to optimization - spend following optimization | |
| Cloud waste indicators |
Idle resources: % of total resources with key features that are not used for any workloads. | # of idle resources / Total resources |
| Orphaned resources: % of total cloud resources not used at all by any teams. | # of unused resources / Total resources | |
| Compression rate: % reduction of compressed file size relative to the original or source file size. | 1 - (# GB after compression / # GB before compression) | |
| Cloud performance indicators | Queries per second: The average number of queries processed per second over a period of time. | Sum of queries processed over a period / Total # of seconds in that period |
| Throughput: The amount of data processed per second over a period of time. | Volume of data processed (in Megabits or Gigabits) over a period / Total # of seconds in that period | |
| Cloud availability indicators | Mean Time To Repair (MTTR): The average time it takes to fully resolve issues and failures. | Sum of repair time over a period / Total # of incidents |
| Availability: % of time cloud services ran error-free and without interruptions. | (Sum of uptime / Total time) x 100 |
What determines a relevant cloud cost KPI for your situation depends entirely on your strategy, tools, and overall business goals. In order to identify what cloud cost optimization KPIs your company should target, it’s essential for your company to have a solid cloud cost optimization strategy in mind.
What is cloud cost optimization as a service?
Cloud cost optimization is a set of practices that companies can implement on their own, but many find it easier to purchase cloud cost optimization tools and strategies as a service. Traditional CCO providers focus on cloud cost visibility and reporting. Other services focus on addressing specific cloud cost management challenges, such as compute utilization, data compression, and data tiering.
Cco-as-a-service pricing
Most providers offering cloud cost optimization services operate on a consumption-based model, meaning that what you pay is based on how much of the service you use. This model is particularly popular with companies operating on a tight budget because they only end up spending based on the company’s usage, making it low-risk.
Additionally, cloud cost optimization providers typically offer prospective clients the following options:
Cloud cost optimization pricing models
| Model | Description | Best for |
|---|---|---|
| Flat fee / Subscription | Monthly or quarterly fee based on a standardized plan issued by the provider. | Companies seeking consistent pricing models to accommodate budgeting concerns. |
| Tiered pricing | Consumption-based payment based on a scale of usage (i.e., number of devices or amount of cloud resources). | Smaller companies with fewer assets to track. |
| Feature-based | An “à la carte” style consumption-based pricing plan in which individual services are purchased. | Companies that already have a good idea of exactly what they need. |
| Seat / User-based | A consumption-based fee is charged per user or agent install, often with discounts for large volumes. | Smaller companies seeking to pay only for what they’re using, and large companies looking for a volume discount. |
| Consulting services | A flat fee is charged for a cloud cost optimization “roadmap” that details needed services. | Companies that are new to cloud cost optimization or that otherwise aren’t sure what services they need. |
| Outcomes-based | Payment is based on measured results, such as cost savings over the course of a contract term. | Organizations looking for a risk-free approach that ensures positive results. |
As for dollar amounts, cloud cost optimization varies widely enough that any amount someone might put in this section would be inherently dishonest; pricing varies according to the pricing model, the needs of the client, and the particular company offering these services.
The best cloud cost optimization management platforms: 2024
As mentioned above, different cloud cost optimization providers address varying cloud cost management challenges, making a direct head-to-head comparison difficult. Many companies must combine several different platforms to build a comprehensive cloud cost optimization strategy. The table below presents some top options and the features provided by each.
The top cloud cost optimization management platforms, 2024
| Company | Features | Pros and cons |
|---|---|---|
| Granica | Cloud data lakehouse compression-based cost optimization Cloud data access operation optimization Cloud data visibility Cloud data privacy Supports open data lakehouse columnar formats such as Apache Parquet |
✔ The only cloud cost optimization platform designed specifically for large-scale data lakehouses and associated storage costs ✔ Automatically identifies and remediates lakehouse storage-related inefficiencies, lowering both at-rest cloud storage costs and cross-region cloud data transfer costs ✔ Speeds up cross-region cloud data transfers, enabling use cases such as disaster recovery, compliance, access to AI-related GPU compute and others ✔ Open, lakehouse-native architecture ensures easy integration into customer cloud environments, without application changes ✔ Risk-free pricing model with 100% ROI guarantee ✘ Does not provide cloud cost allocation and other traditional cost management features |
| Apptio Cloudability | Cloud cost allocation Resource identification/tagging Business mapping Visualizations and reports Cloud budgets and forecasting |
✔ Provides resource identification, cost allocation, and other key CCM features ✔ Automates business mapping, cost anomaly detection, cloud cost chargeback, and block storage management ✔ Offers robust dashboards, visualizations, and reports for single-pane-of-glass cloud cost visibility ✘ Tiered, cloud-spend-based pricing model makes the platform more expensive the more it’s needed ✘ Forecasting feature is limited to only showing forecasts per service, not per account |
| VMWare Tanzu CloudHealth | Resource organization and management Reporting and dashboards Budget management and forecasting Cost allocation and chargeback Resource right-sizing Anomaly detection Migration planning |
✔ Provides robust resource management and cost allocation capabilities ✔ Includes Kubernetes cost optimization as well as GreenOps reporting to help reduce carbon footprints ✔ Easy to configure and use ✘ Price increases alongside your other cloud expenses ✘ Often experiences connectivity and speed issues |
| AWS Cost Explorer | Cost allocation Business insights Cost and usage forecasting Customized dashboards and reports |
✔ Manages AWS costs and usage over time ✔ Allows companies to filter and group data, visualize daily or monthly costs, and forecast future costs ✔ Provides a customizable dashboard for visualizing costs ✘ Price increases alongside your other cloud expenses ✘ Only works with AWS environments |
| Google Cloud Cost Management | Resource hierarchy and access control Reports and dashboards Budgets with automatic alerts Recommendations and insights |
✔ Displays the entire Google Cloud environment at-a-glance from a series of dashboards ✔ Offers specific recommendations for right-sizing resources ✔ Provides insights into improving workflows and forecasting budgets ✘ Price increases alongside your other cloud expenses ✘ Only works with Google Cloud environments |
Finding the right cloud cost optimization option for your company can be an overwhelming process. Even for experienced parties, the prospect of identifying underutilized or orphaned resources, appropriately right-sizing them, and tracking your progress creates a huge margin for error. This is often followed by long trial-and-error periods as you work systematically through your cloud cost optimization strategies to identify problems and fix them.
For that reason, many companies choose to partner with one or more CCO platforms that simplify and automate many cloud cost optimization workflows. Traditional cloud cost optimization tools focus on identifying cloud costs and resolving inefficiencies in compute-oriented resource and service utilization, leaving a huge gap when it comes to large-scale, data-oriented resource optimization. For companies using data-heavy applications like artificial intelligence and machine learning, the skyrocketing cost of cloud data lake storage is a major concern that a comprehensive cloud cost optimization strategy must address.
Cloud cost optimization with Granica
Granica provides a comprehensive platform for making large-scale cloud data ready for AI, with specific services for cloud cost optimization, data privacy, and data visibility. Granica services are optimized for tabular and natural language processing (NLP) data sets, especially data sets used with traditional and generative AI for training and inference. Granica supports such data sets in cloud object storage-backed data lakes and lakehouses.
Our experts are here to advise you on how best to leverage Granica Crunch to control the cloud costs for your lakehouse Parquet data, offered with a risk-free 100% ROI guarantee. Crunch uses advanced compression optimization technology that physically shrinks Parquet files in the cloud by up to 60%. By reducing the size of the files, Crunch reduces the costs associated with at-rest cloud storage as well as the cost and time associated with cross-region cloud data transfers, helping you meet your most crucial cloud cost optimization KPIs for both cost and performance.
We know that data is your most valuable asset, and cloud cost optimization techniques must not interfere with your data’s quality, privacy, or security. Our cloud cost optimization capabilities, and broader AI data readiness solutions, treat your data with the care it deserves to not only improve cost efficiency but also data privacy and utility, which leads to optimized downstream performance for analytical, machine learning, and generative AI applications.
Sign up for a demo of Granica’s cutting-edge, AI-powered cloud cost optimization solutions to take the next step in your CCO journey.
Thoughts? Leave us a comment below: