Cloud computing offers organizations unsurpassed opportunities to improve the agility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness of their digital operations. However, recent research suggests that only 30% of companies know exactly what they’re paying for in the cloud, which makes it difficult to keep costs in check or ensure operational efficiency. Various factors like under-utilized cloud resources, surging data growth, and hidden fees all contribute to the challenges many companies face in planning and managing cloud budgets.
Cloud cost management (CCM) is a combination of tools and strategies organizations use to reduce cloud spending and improve efficiency. This guide explains what CCM is and why it’s essential to businesses before discussing some cloud cost management best practices that can help you control expenses.
What is cloud cost management, and why is it essential?
Cloud cost management (or cloud cost optimization) involves analyzing cloud infrastructure, services, and applications to ensure a company is only using the resources it actually needs. Recurring cloud costs can be unpredictable because of auto-scaling and the ability to add new features to your cloud service with the click of a button. Other factors that contribute to ballooning cloud costs include:
![]() Under- or mis-utilized cloud resources.
Allocating more CPU power, storage capacity, or features than needed for a particular workload, and purchasing more for new instances rather than reallocating existing resources.
Under- or mis-utilized cloud resources.
Allocating more CPU power, storage capacity, or features than needed for a particular workload, and purchasing more for new instances rather than reallocating existing resources.
![]() Poor data governance.
Paying to store redundant or irrelevant data in cloud data lakes because you lack the tools or policies for identifying, categorizing, losslessly compressing, and intelligently deleting cloud data.
Poor data governance.
Paying to store redundant or irrelevant data in cloud data lakes because you lack the tools or policies for identifying, categorizing, losslessly compressing, and intelligently deleting cloud data.
![]() Hidden fees/complex billing.
Adding cloud features without understanding all the fees involved, having different payment schedules for each cloud vendor or service, and lacking the ability to predict usage fluctuations.
Hidden fees/complex billing.
Adding cloud features without understanding all the fees involved, having different payment schedules for each cloud vendor or service, and lacking the ability to predict usage fluctuations.
![]() Shadow IT.
When individual departments or users purchase the cloud services they need without notifying IT or researching whether an existing tool could handle their workflow.
Shadow IT.
When individual departments or users purchase the cloud services they need without notifying IT or researching whether an existing tool could handle their workflow.
![]() Surging data growth.
Continuously generating and storing more data in the cloud, especially in data lakes and data mesh environments for business intelligence analytics and AI/ML training use cases, inflating monthly data storage costs.
Surging data growth.
Continuously generating and storing more data in the cloud, especially in data lakes and data mesh environments for business intelligence analytics and AI/ML training use cases, inflating monthly data storage costs.
CCM teams eliminate or reallocate resources as needed to reduce costs and better support the business. In addition, cloud cost management aims to optimize cloud-based operations to improve performance, reliability, and workload efficiency, all of which give organizations a better return on their cloud investments.
6 Cloud cost management best practices
The following cloud cost management strategies can help organizations reduce inefficiencies and lower their recurring cloud costs.
1. Right-size your cloud resources to reduce usage
Cloud compute resource utilization (a.k.a. CPU and GPU power) is typically one of the largest cloud expenditures, so any inefficiencies can significantly increase your recurring cloud costs. For example, IT teams often provision new cloud instances with more compute power than they need for a given task, which quickly increases the hourly unit cost above what’s actually required. Many teams also forget to stop old instances, or they purchase new ones rather than repurposing the remaining unused instances, all of which can drive the total costs up.
Right-sizing your cloud instances involves identifying and eliminating utilization inefficiencies so CPU and GPU resources can be reallocated or stopped to reduce recurring costs. Although IT teams could track cloud utilization manually, such inefficient practices are prone to human error. Using a cloud cost management tool helps automate this process with features like resource discovery and utilization monitoring.
2. Take advantage of commitment-based discounts
Reserved instances (RIs), Savings Plans, and other commitment-based discounts allow customers to reserve a certain capacity in a specific region for a pre-determined length of time (usually one or three years). These discounts offer significant savings without changing your underlying infrastructure, which makes them a great top-line strategy for cost reduction.
However, long-term commitments come with downsides, like being locked into a cost schedule even if a provider cuts prices, with no options to upgrade or scale on-demand. AWS allows customers to sell off their RIs on Amazon’s Reserved Instance Marketplace, where other companies can buy RIs at an even steeper discount.
3. Losslessly compress data for data lake cost reduction
Cloud data lake storage presents another major cloud cost. Surging data growth – when combined with automatic scaling – can make recurring cloud bills extremely unpredictable. Identifying high-priority data is extremely challenging, especially in data lake and data mesh environments. Many teams just don’t have the time or technology to sort through volumes of data with the required precision to maintain AI training quality or meet compliance requirements. Often choosing to err on the side of caution, many firms simply keep everything and place that data in the most expensive storage class or tier.
Data compression decreases cloud storage costs by losslessly reducing the physical size of data files, especially the Apache Parquet files which form the foundation of cloud data lakes and lakehouses. This lowers the effective unit cost of cloud data lake storage while keeping data in its existing tier. With lossless data compression, organizations can keep data in the “standard” tier with full availability SLAs, and still manage costs down. Compression offers other potential benefits, like improved performance for I/O bound applications, faster data transfer, and a lower carbon footprint.
However, the act of compressing and decompressing data as it is read takes time, and also costs compute. Most off-the-shelf compression tools aren’t optimized for speed, cost, and scale in the cloud, so it’s important to use enterprise-grade lossless compression tools optimized for cloud data lakehouses to maintain scalability and even improve data processing performance.
4. Use data tiering to further reduce data lake storage costs
Sometimes, data compression alone isn’t enough to reduce cloud data lake costs to the desired level. The practice of data tiering prioritizes data according to urgency and importance and moves it to the appropriate storage location. For example, the data you’re actively using for AI training and analytics should stay in expensive “hot” storage, whereas data for compliance or other recordkeeping purposes can be moved to less expensive “cold” storage.
Some cloud providers offer automated data tiering, such as AWS S3 Intelligent Tiering, which moves data based on the time since the last access. However, lower-tiered data has lower availability than “standard” data, which is why many organizations want to keep as much data as possible in the standard tier. Because standard storage costs more, however, CCM teams should pair data tiering with compression to help lower expenses.
Estimate cloud cost savings with our online calculator.
5. Track cloud spending across departments
Many cloud services are user-friendly enough that individual departments can purchase and deploy them without any intervention from IT teams. This scenario is known as “shadow IT,” which often creates the following risks and inefficiencies:
-
When cloud services aren’t properly configured or onboarded, IT teams can’t patch vulnerabilities, monitor for potential breaches, or deploy security tools to protect them.
-
A department might purchase a new tool when the company already pays for a cloud service that provides the same capabilities.
-
IT teams may have an incomplete understanding of how much the company truly spends on cloud infrastructure and services, which makes it difficult to create accurate budgets or implement effective cost-management strategies.
To fully realize the efficiency and cost-saving benefits of cloud cost management, you need a reliable tracking method for cloud usage and spending across departments. Cloud discovery tools can help by identifying all the applications and services in use by an organization. Some cloud cost management platforms also offer features like cost allocation tags so IT can track cloud spending by department, workload, or other helpful categories.
6. Streamline CCM workflows with a cloud cost management tool
Organizations can choose from a variety of available software tools and platforms to assist with the cloud cost management strategies listed above. No single platform offers every component, so many companies combine two or more tools to cover all the capabilities they require. Below, we list some examples of the most popular cloud cost management tools and the features they provide.
Top cloud cost management tools in 2024
| Platform | Key Features | Supported Clouds |
|---|---|---|
| Granica |
|
|
| Apptio Cloudability |
|
|
| NetApp Cloud Volumes ONTAP |
|
|
| NetApp Spot Eco |
|
|
| Tanzu CloudHealth |
|
|
For more in-depth reviews of the best CCM software, read our comparison of the Top Cloud Cost Management Tools in 2024.
Cloud cost management with Granica
The preceding tools and strategies can help your business reduce overall cloud spending, operate more efficiently, and support sustainable growth and innovation. While other cloud cost management platforms on the list focus on allocating cloud costs and optimizing compute resource utilization, they leave a big gap when it comes to large-scale cloud data management.
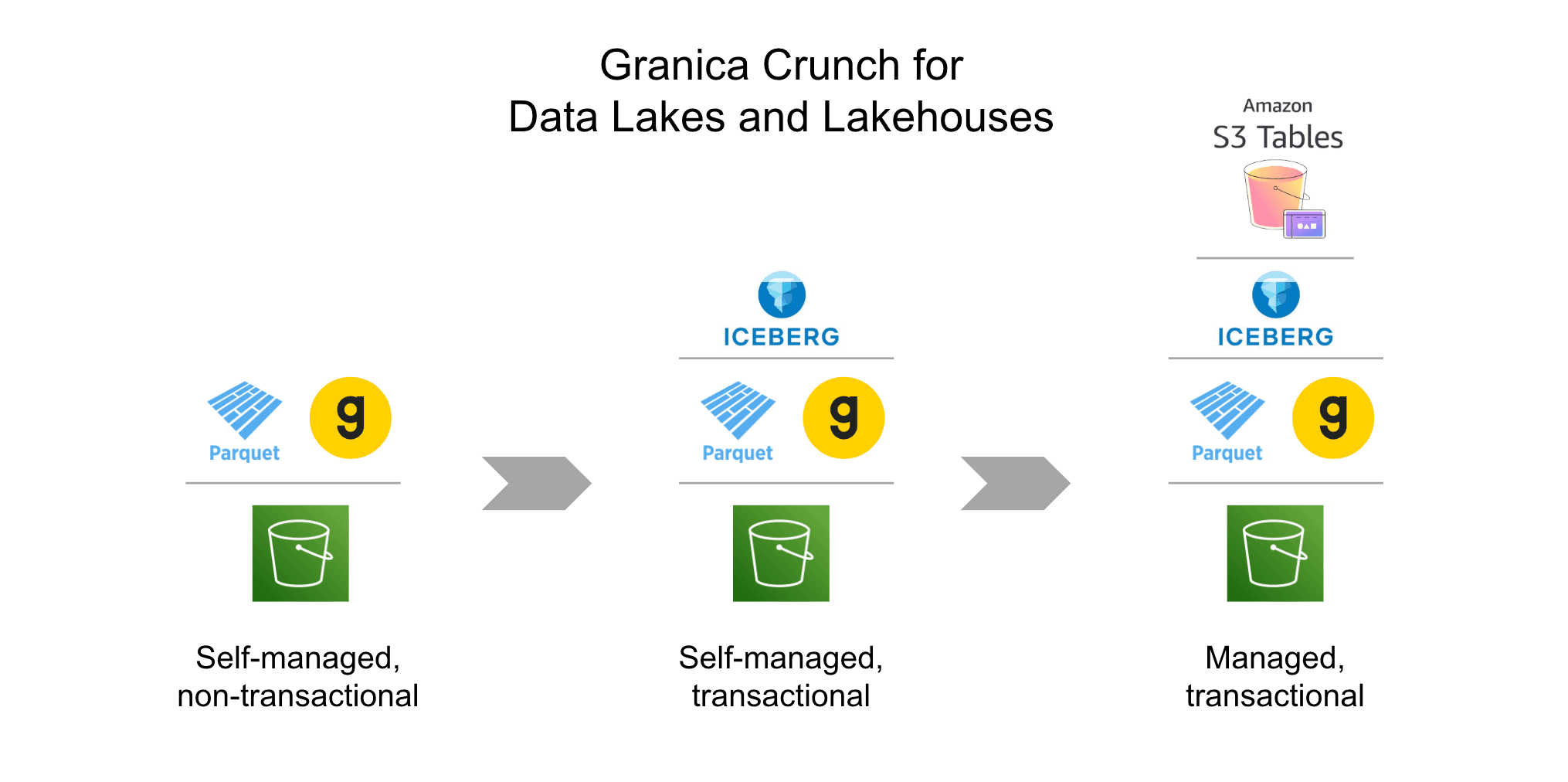
Granica fills this gap with a data management platform that reduces cloud object storage costs for large-scale analytics and AI training data sets in cloud data lakes and lakehouses. Granica Crunch is the world’s only cloud data lake compression optimizer. It works within Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Google Cloud environments, where it uses novel, proprietary optimization techniques to transparently reduce the physical size of the Apache Parquet files which are the foundation of large-scale cloud data lakehouses. Crunch-optimized Parquet files are not only smaller and save money, they are faster to read and improve data processing speeds.
Request a free demo to learn how Granica’s cloud cost management tools can help you reduce cloud data lake storage costs by up to 60%.