According to Microsoft, 86% of organizations take a multicloud approach of using two or more public cloud platforms to run their various digital services. While multicloud environments can help companies maximize scalability, availability, and agility, they can also be extraordinarily challenging for keeping costs in check. Factors like shadow IT, underutilized/mis-utilized resources, and surging data growth – not to mention a lack of centralized cost management – can all cause multicloud expenses to spiral out of control. Moving bulk data between clouds for AI training, analytics, or disaster recovery also drives up cloud data transfer costs, catching companies that lack centralized management by surprise.
This blog post discusses four multicloud cost management strategies and tools that companies can use to help make their cloud services run more cost-effectively and take full advantage of their multicloud architecture.
4 Multicloud cost management strategies
The following strategies and tools can help organizations identify and reduce multicloud expenses.
1. Track spending across departments and clouds
All cloud deployments run the risk of shadow IT, a scenario in which individual business units purchase and deploy their own cloud services without notifying the IT department. The risk is even greater in multicloud environments because it’s harder for IT teams to track which features or services are allocated to which platform.
Cloud cost allocation involves discovering and tagging all cloud services in use across the organization so teams can see where their monthly costs are coming from. The major cloud platforms like AWS and Azure include their own, single-platform cost allocation tools, while third-party solutions like Apptio Cloudability provide centralized cost allocation for multi-vendor, multicloud deployments.
2. Right-size cloud resources to reduce waste
Cloud providers charge usage-based fees for compute resources like CPUs and GPUs. Typically, these fees represent an organization’s largest cloud expenditures. Inefficient resource utilization – provisioning new instances with more power than necessary, or forgetting to stop old instances, for example – is a major driver of unnecessary multicloud costs.
Right-sizing cloud resources by identifying and eliminating inefficient instances is a great top-line method for managing costs. Although organizations can perform this task manually, using tools like VMware Tanzu CloudHealth can automate the process to reduce the risk of human error and improve productivity.
3. Compress cloud data to reduce storage and transfer costs
Cloud data storage can be another significant multicloud cost driver. Data-hungry applications like AI, machine learning, data science, and analytics all contribute to spiraling data storage costs, especially in unstructured cloud data lakes and lakehouses.
Data tiering and archival strategies are the traditional solution, moving less-usable data to cheaper cold storage solutions for savings, but identifying which data is needed most urgently, and which can be safely archived, can be extremely time-consuming and prone to errors. Plus, data teams and cloud architects often prefer to keep the vast majority of their data in the expensive standard tier where it’s easily accessible, has the highest SLA, and incurs the fewest data transfer charges, which limits the amount of money actually saved.
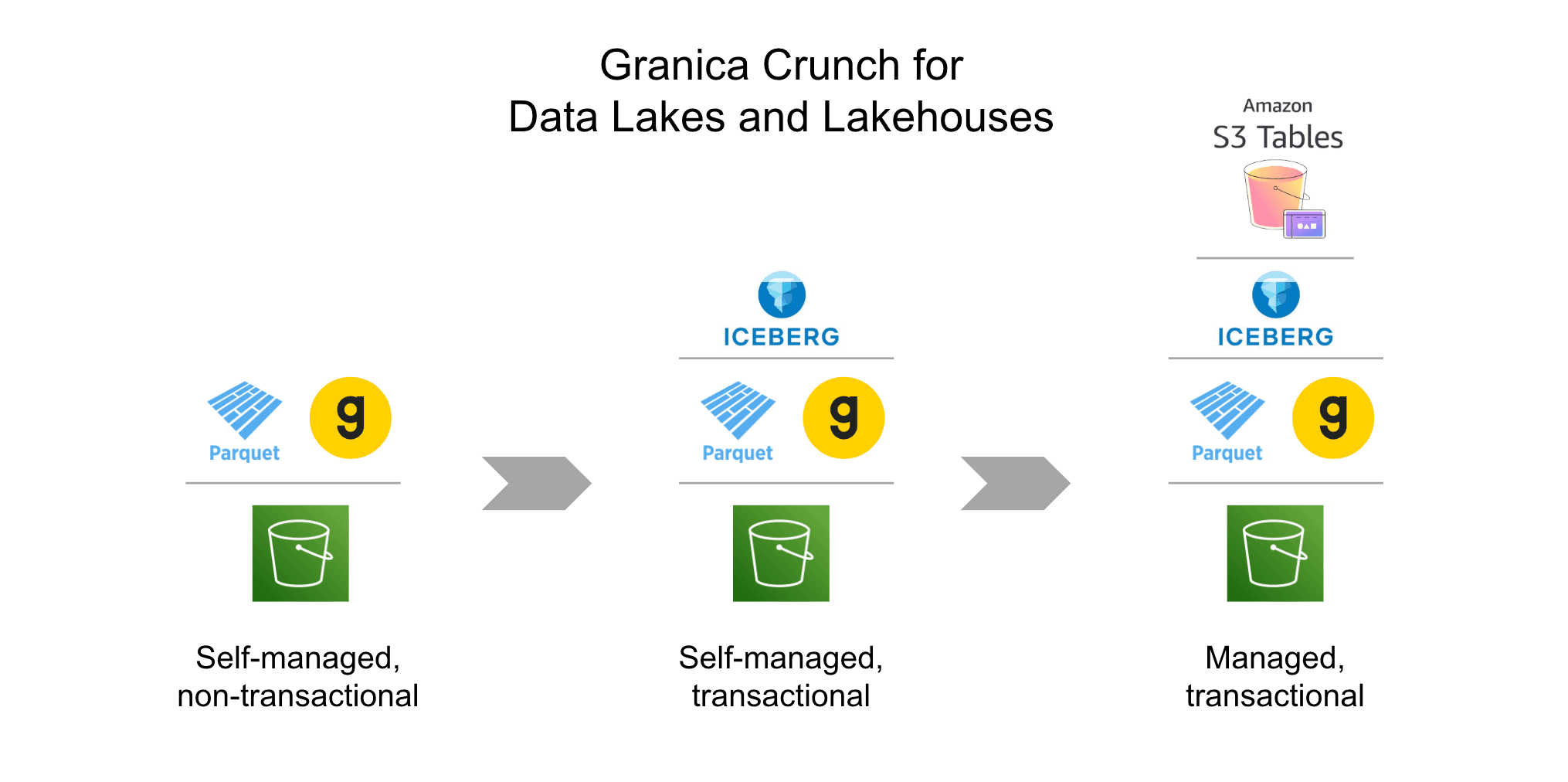
Data compression is a better multicloud cost management strategy for data-heavy use cases because it makes data available for applications while reducing storage expenses. Compression shrinks the physical bit size of data at rest and in transit, which lowers the effective unit cost of cloud data storage and transfer. While compressing and decompressing data as it’s read can be time- and compute-consuming, tools like Granica Crunch use compute-efficient compression optimization techniques which both lower costs and speed up data access and processing.
4. Take advantage of commitment-based discounts
Reserved instances (RIs), Savings Plans, and other platform-specific commitment-based discounts let you reserve a certain capacity of resources for a pre-determined length of time in exchange for reduced monthly costs. Since these discounts can deliver significant savings without changing your underlying infrastructure, they offer another excellent top-line strategy for multicloud cost management.
On the other hand, you may subsequently learn through the other strategies on this list that you don’t actually need as much compute or storage as you once thought. If you’re locked into a minimum provider commitment of one to three years, you’ll have little to no recourse for cutting costs any further. It’s important to consider these trade-offs before deciding how to proceed with your cloud cost management implementation.
Multicloud cost management with Granica
Granica is an AI data readiness platform for multicloud environments across Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Google Cloud. Granica Crunch helps reduce cloud object storage and cross-cloud data transfer costs for large-scale AI, ML, data science, and analytics data sets in cloud data lake and lakehouse environments. Crunch is the world’s only lakehouse-native compression optimizer. It transparently reduces the physical size of the Apache Parquet files which form the data foundation of large-scale cloud data lakehouses.
Click here for an interactive demo of the Granica Crunch multicloud cost management platform.